Introduction to Granny Chargers
In the realm of electric vehicles (EVs), the usage of granny chargers often poses a practical challenge for users. These chargers, colloquially known as “granny cables,” serve as portable charging solutions for EVs, facilitating slow charging through standard UK domestic sockets. The name “granny charger” may evoke curiosity, but it aptly describes a charger typically used for EV charging when access to dedicated home or public charging stations is limited, such as when visiting relatives or embarking on road trips.
Granny chargers feature a standard UK household electrical 3-pin plug on one end, compatible with domestic sockets, and an EV connector (commonly Type 1 or Type 2) on the other end, facilitating the connection to the EV. Despite their practicality, the cable length of granny chargers often falls short, prompting users to explore the possibility of using extension leads to bridge the gap. However, this raises questions regarding safety, compatibility, and optimal usage, which we aim to address comprehensively in this guide.
Understanding the Debate: Safety Concerns
One of the most debated topics surrounding granny chargers is the use of extension leads. Manufacturers and EV enthusiasts often engage in discussions regarding the safety implications of using extension leads with granny chargers. Many manufacturers advise against using extension leads due to safety concerns, primarily stemming from the absence of dedicated safety features in domestic sockets.
Unlike dedicated EV sockets, domestic sockets may lack crucial safety mechanisms such as Residual Current Devices (RCDs) and earth rod protection. These safety features are essential for protecting against electrical faults and ensuring user safety during the charging process. Consequently, using extension leads with granny chargers connected to domestic sockets may pose inherent risks, warranting caution and careful consideration.
Cable Specifications and Material Durability
Beyond safety concerns, the specifications of extension leads play a pivotal role in determining their compatibility with granny chargers. Most extension leads available in the market are manufactured using cables with insufficient diameter to handle the relatively high sustained current required for EV charging, typically around 10A. The diameter of the cable directly influences its capacity to transmit electricity efficiently and safely.
Furthermore, the length of the extension lead impacts its ability to sustain the flow of electricity, drawing a parallel to the concept of water flow through a pipe. Longer distances necessitate thicker cables to maintain the same level of electrical conductivity and minimize power loss. Therefore, users must carefully evaluate the specifications of extension leads, ensuring they meet the requirements for safe and effective EV charging.
In addition to cable specifications, the material and durability of extension leads are critical factors to consider. Many extension leads utilize PVC or “arctic” flex cables, which may not be suitable for outdoor use or adverse weather conditions. These cables are susceptible to mechanical damage and degradation, posing risks to user safety and compromising the longevity of the charging setup. Thus, users must prioritize the selection of extension leads made from durable materials capable of withstanding the rigors of EV charging environments.
Benefits and Limitations of Granny Chargers
Granny chargers offer undeniable benefits in terms of portability and convenience, allowing EV owners to charge their vehicles wherever standard domestic sockets are available. However, these chargers also come with inherent limitations, particularly concerning safety standards and charging efficiency.
While granny chargers serve as practical backup solutions for occasional charging needs, they may not offer the same level of efficiency and safety as dedicated home EV chargers. Unlike dedicated chargers, granny chargers lack advanced features such as load balancing and smart connectivity, limiting their suitability for everyday charging requirements. Therefore, while granny chargers provide flexibility, they may not be the optimal choice for users seeking faster, more efficient, and safer charging solutions.
Choosing the Right Charging Solution
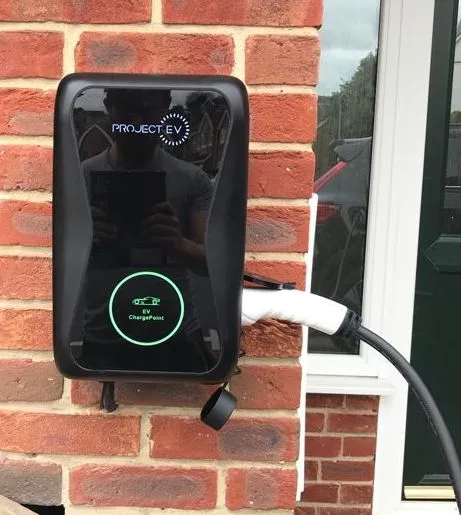
Given the considerations outlined above, selecting the appropriate charging solution becomes paramount for EV owners. While extension leads may offer temporary solutions for extending the reach of granny chargers, they may not provide the safety and performance standards required for regular EV charging. Thus, investing in a dedicated home EV charger emerges as the preferred option for optimal charging efficiency and safety.
Home EV chargers offer numerous advantages over granny chargers, including higher charging speeds (typically 7kW), smart features for enhanced control and monitoring, and superior safety standards. These chargers are specifically designed to withstand harsh weather conditions and provide reliable charging solutions for daily use. Additionally, home EV chargers allow users to schedule charging sessions during off-peak hours, maximizing cost savings and efficiency.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Safety and Efficiency
In conclusion, the debate surrounding the use of extension leads with granny chargers underscores the importance of prioritizing safety and efficiency in EV charging practices. While extension leads may offer temporary solutions, they may not meet the necessary safety standards for regular use with granny chargers. Therefore, investing in a dedicated home EV charger remains the optimal choice for EV owners seeking faster, more efficient, and safer charging solutions.
Ultimately, EV owners must carefully assess their charging needs, prioritize safety considerations, and invest in charging solutions that align with their requirements and usage patterns. By prioritizing safety and efficiency, EV owners can enjoy seamless and reliable charging experiences while minimizing risks and ensuring long-term satisfaction with their EV charging setups.