Understanding 3 Phase Electricity in the UK
Wondering about 3-phase electricity in the UK? This guide is here to help! Whether you’re a home owner, business owner, or just curious, it will explain everything you need to know.
Why is 3-phase important? In the UK, it’s the go-to power source for businesses and factories because it’s more powerful and efficient than single-phase.
But how does it work? We’ll break down the technical details, explaining the three phases and their voltage differences.
Where is it used? We’ll also explore how 3-phase powers things like electric motors and machinery in various industries. With its growing importance, understanding 3-phase empowers both electricians and home owners to make informed decisions about their electrical systems.
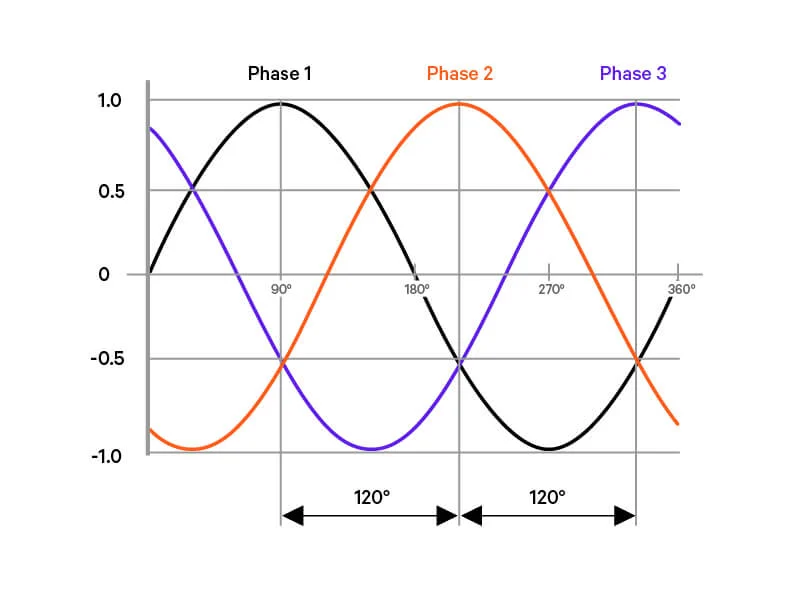
How does 3 phase electricity work?
Let’s start with the basics:
- Single-phase: This system uses two wires: a live wire and a neutral wire. The voltage goes up and down like a wave.
Now, for 3-phase:
- Three live wires: Each carries electricity, but their “peaks” are shifted by 120 degrees (denoted as A, B, and C). This creates a smoother, more constant flow of power.
- Benefits of this setup:
- Balanced load: The power is evenly distributed among the three phases, reducing stress on each wire.
- Higher power capacity: This system can handle more power, making it ideal for demanding applications.
- Steady supply: The constant waveform provides a reliable and smooth flow of electricity, especially crucial for industrial settings like factories and data centers.
Advantages of 3 phase electricity
3-phase electricity shines in two main ways compared to single-phase:
1. Handles more power: With three “lanes” for electricity to flow, 3-phase spreads the load efficiently, reducing strain on wires and equipment. This makes it perfect for powering heavy duty machinery in factories.
2. Balanced and efficient: The power is evenly distributed among the three phases, lowering the load on each wire. This not only improves overall efficiency but also lowers the risk of over loading or voltage drops.
Bonus perk: 3-phase motors run smoother, generate less heat, and are more powerful than single-phase motors. This makes them ideal for demanding tasks like powering pumps, compressors, and conveyor belts.
Differences between single phase and 3 phase electricity
The key differences between single phase and 3 phase electricity come down to power and how they deliver it:
- Power: Single phase offers less power, usually around 230 volts in the UK, while 3 phase provides significantly more, ranging from 400 to 415 volts.
- Waveform: Single phase has a wavy, up and down pattern, while 3 phase has a smoother, more consistent flow. This stability is vital for sensitive equipment needing a steady power supply.
- Load: Single phase systems can have uneven distribution, leading to inefficiencies. 3 phase, however, distributes the load equally, making it more efficient and reliable.
Common applications of 3 phase electricity
Many industries use 3-phase electricity because it’s powerful and efficient.
Factories: 3-phase powers big machines like pumps, compressors, and conveyor belts. It keeps the power flow smooth and can handle high electrical demands.
Buildings: 3-phase runs large buildings like offices, hospitals, and shopping centers. It provides the power needed for air conditioning, elevators, lights, and other equipment.
Construction: Construction sites use 3-phase for machinery, tools, and temporary power. It delivers the extra power needed for demanding tasks.
Renewable energy: Sources like wind and solar often generate 3-phase electricity. This makes it easier to connect them to the existing power grid and use the clean energy they produce.
Understanding the phases and voltage in the UK
3-phase electricity in the UK comes in two voltages:
- Line-to-line: 400-415 volts (between two phases).
- Line-to-neutral: 230 volts (between a phase and the neutral wire).
Each phase (L1, L2, L3) has its own balanced voltage for optimal performance and safety. Understanding these voltages is important for working with 3-phase equipment for proper installation and use.
Safety
When working with 3-phase electricity, safety is important. Here’s what you need to know:
1. De-energize before touching: Always turn off the power and isolate the circuits before working on any electrical components. Use tags to clearly mark the isolation.
2. Gear up: Wear insulated gloves, safety glasses, and flame resistant clothing to protect yourself from shocks and arc flashes.
3. Lock it out: Use lockout or tagout procedures to prevent accidental energization. This means using devices and tags to indicate that equipment is being worked on and shouldn’t be switched on.
4. Maintain regularly: Regularly inspect and maintain your electrical equipment for loose connections, damaged insulation, or over heating to address potential hazards.
By following these safety guidelines, you can avoid electrical accidents and create a safe working environment when dealing with 3-phase electricity.
Upgrading to 3 phase electricity in the UK
If you’re considering upgrading to 3 phase electricity in the UK, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, determine your power requirements and consult with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer to assess the feasibility of the upgrade.
Next, contact your local distribution network operator (DNO) to discuss the process and requirements for connecting to the 3 phase grid. This may involve submitting an application, obtaining necessary permits, and meeting specific technical standards.
Additionally, upgrading to 3 phase electricity may require modifications to your electrical system, including the installation of a 3 phase distribution board and appropriate wiring. It’s crucial to hire a professional electrician to ensure proper installation and compliance with electrical regulations.
Cost
Upgrading to 3-phase electricity varies in cost, depending on your location, power needs, and current wiring. Expect to pay for connection fees, installation, and any needed upgrades.
While the upfront cost might be higher than single-phase, 3-phase offers more power and efficiency, making it a good long-term investment. Consult with professionals to weigh the costs and see if 3-phase is right for your needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of 3-phase electricity is important for anyone working with electrical systems, whether they’re professionals or home owners. 3-phase offers more power, balances loads better, and saves energy, making it ideal for businesses and factories.
As technology advances with electric cars, renewable energy, and smart grids, the need for reliable and efficient power is growing. Staying informed about the latest in 3-phase electricity helps individuals and businesses adapt to the changing needs of the electrical industry.
In short, 3-phase electricity is key to the UK’s electrical power. By learning how it works, its benefits, uses, and safety, you can make informed choices for your electrical system, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Financial Perks of Electric Vehicles
Challenges in EV Battery Supply
Installing EV Chargers at workplace










I have been browsing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me. Personally, if all site owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the web will be a lot more useful than ever before.
I have recently started a blog, the information you provide on this website has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work. “It is a great thing to know our vices.” by Cicero.
As I website possessor I believe the content here is real fantastic, thanks for your efforts.
Hey there would you mind sharing which blog platform you’re working with? I’m planning to start my own blog in the near future but I’m having a difficult time selecting between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your design and style seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something unique. P.S My apologies for getting off-topic but I had to ask!
You are a very intelligent person!
I do enjoy the manner in which you have presented this specific situation plus it does present us a lot of fodder for consideration. Nonetheless, through what precisely I have observed, I just simply wish as the reviews pack on that people remain on point and not start upon a soap box associated with the news du jour. All the same, thank you for this excellent piece and whilst I do not really agree with the idea in totality, I regard the standpoint.
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Thank you for your provided information.
priligy 60 mg price Cabozantinib, sold under the brand names Cometriq and Cabometyx, is a medication used to treat medullary thyroid cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and hepatocellular